 |
| Linux File System |
A file system is a method of storing and organising arbitrary collects of data in a form that is human-readable. A file system organizes data into an easy to manipulate database of human readable names for the data ,usually with a human readable hierarchical organization of the data ,for the storage ,organisation ,manipulation and retrieval by the computer OS (operating system). Each discrete collection of data in a file system is referred to as a computer.File system are used on data storage devices such as hard disk -CD ROMs to maintain the physical location of the files.
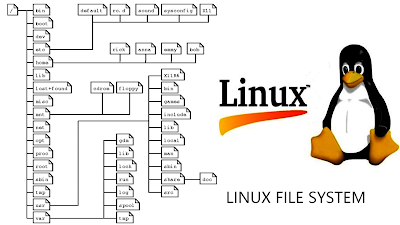
The “trunk” of the tree is the root directory.
The root directory is simply identified as a”/”.
All other directories “branch” Off from the trunk.
The tree of the file system starts at the trunk or slash, indicated by a forward slash (). This directory ,containing all underlying directories and files is also called the root directory or the “root” of file system.
Directories that are only one level below the root directory are often preceded by a slash ,to indicate their position and prevent confusion with others directories that could have the same name. When starting with a new system ,it is always a good idea to take a look in the root directory.
the following lists the most common directories and their intended contents.
/ – root directory.
/home – where directories are contained for each other.
/usr – pronounced ‘user’ and contains Linux commands and utilities.
/bin – binary executable programs.
/lib – program libraries ,similar to windows ‘dll’ files
/sbin – move executable programs and linux utilities for administrative purpose.
/doc – documentation
/src – source code to programs
/tmp – temporary code to programs.
/etc – configuration files.
/rc.d – scripts used during boot and shutdown process.
/sysconfig – default.
/sysconfig/network scripts – network scripts
/sysconfig/daemons – special programs that run in background ,such as print spooling.
/bin – binary executable programs that all users need.
/dev – device files that control drives ,terminal and any equipment attached to the server.
/var – user specific files.
/log – files containing system usage and errors
/spool where spooled files are stored during print spooling process
/mail – where Email files are stored until retrieved by client Email program
/proc -system files.
/root – root’s home directory
opt – others options
/sbin – more executable program and utilities.
Important files and Directories
The Shell is a UNIX term for the interactive users interface with an operating system. The shell is the layers of programming that understands and executes the commands a users enters. In some systems ,the shell is called a command interpreter.
Shell is a software program that allows you to interact and access a computer system. User can enter commands in the shell prompt, which will be executed by the shell. Since the only means of communication through shell is test ,it is known as Command-Line-Interface or CLI.
Types of Shell – there are different types of shells in Linux and UNIX each shell work is different from each other-
- sh or Bourne Shell : This shell is used in UNIX and in Unix related environments.Sh shell is basic shell and has a few features.
- bash or bourne again shell : It is a standard GNU shell, Intuitive and flexible. Probably tool the most advisable for beginning users while being at the same time a powerful tool for the advisable for beginning users while being at the same time a powerful tool for the advanced and professional user. On Linux ,bash is the standard shell for common users. This shell is so-called superset of the bourne shell, a set add-ons and plug-ins. This means that the bourne again shell is compatible with the bourne shell ; commands that work in sh, also work in bash.
- csh or C shell : this shell is used for C programming.
- tcsh or TENEX C shell : this is a advanced version of c shell and it is also called TURBO C.
- ksh or the Korn Shell : Sometimes appreciated by people with UNIX background. A superset of the bourne shell ; with standard configuration a nightmare for beginning users.


